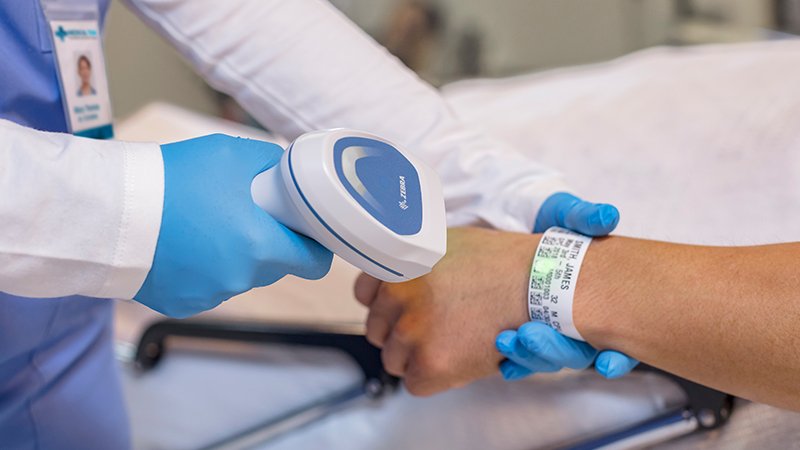
Reading barcodes on things like patient wristbands, medicines, and tools is called barcode scanning in healthcare. This is done to get important information for different healthcare processes. Barcodes are an important way to make sure that patients are who they say they are, that medications are given correctly, and that hospital assets are tracked. As reading gets better, barcodes play an even bigger role in healthcare than they did before. When you hear the word “barcode,” you might first think of stores. However, hospitals and other healthcare facilities can also use them.
Enhancing Patient Identification
A lot of hospitals keep track of patient information with barcodes. Doctors and nurses can get information about patients with just one scan of the wristbands that have barcodes on them. They can keep the records up-to-date and change them as they treat the patient. In situations where the patient needs care right away, this process can save lives. It also speeds up care, which lets doctors help more people.
This simple yet effective measure drastically reduces the chances of medication errors, which are among the most common and potentially dangerous mistakes in hospitals. A report by the World Health Organization highlights that medication errors alone harm millions of patients annually. Hospitals can minimize the risk of adverse drug events by administering medications to the correct patient, in the correct dose, and at the correct time by using barcode scanning technology.
Effective Medication Administration
Barcode scanners also streamline the medication administration process, making it safer and more efficient. Nurses can scan the barcode on a medication vial or packaging and cross-check it against the patient’s electronic medical records. This procedure ensures that the medication matches the physician’s prescription and is safe for the patient, taking into account any allergies or potential drug interactions.
This technology not only helps prevent errors but also saves time for healthcare providers. Instead of manually verifying medication details, nurses and doctors can quickly confirm all necessary information with a simple scan. This efficiency allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care, increasing overall satisfaction and safety.
Improving the Safety of Blood Transfusions
Biological products, like blood, must often be handled in order to diagnose and treat medical problems. Using barcodes on blood and blood-related items that are meant to be transferred has been proven to improve patient safety and accuracy, taking advantage of how well barcode technology works. When it comes to lab testing, barcodes are very important because they let workers keep a close eye on samples and track them down to enter into the laboratory information management system, which ensures accurate and reliable test results.
Supporting Inventory Management and Infection Control
In addition to improving patient safety, barcode scanners are instrumental in managing hospital inventory. Tracking medications, blood products, and medical supplies with barcodes helps hospitals maintain accurate inventory levels, ensuring that critical items are always available when needed. Efficient inventory management also minimizes waste and reduces costs, contributing to a more sustainable healthcare system.
Barcode scanners also support infection control efforts. For instance, the process of scanning medical equipment and devices before and after use guarantees their proper sterilization, thereby lowering the risk of hospital-acquired infections. By maintaining a digital record of equipment usage and sterilization, hospitals can better adhere to hygiene protocols and quickly identify any lapses in infection control.
Future of Barcode Scanning in Healthcare
As technology continues to evolve, the future of barcode scanning in healthcare looks promising. Advances in wireless scanning, integration with electronic health records, and the development of more sophisticated barcode systems will likely further enhance patient safety and operational efficiency in hospitals.